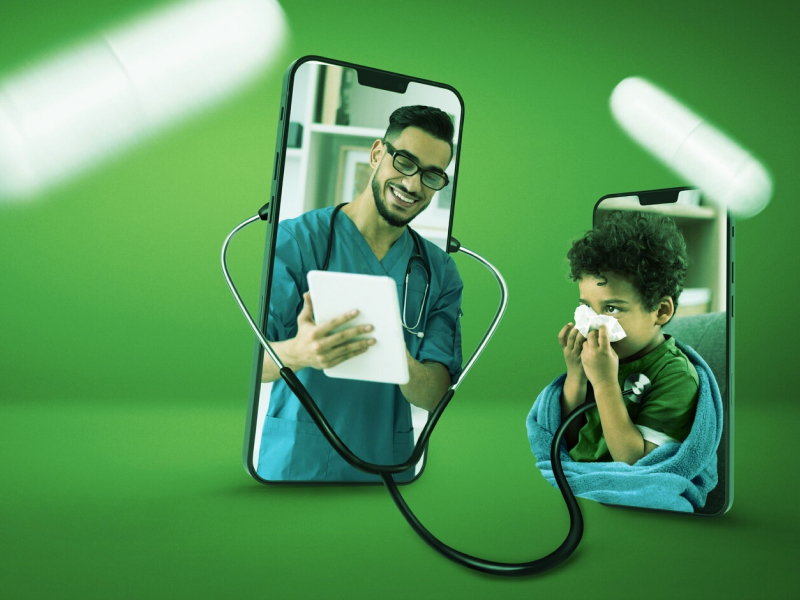
With a valuation of $52.33 billion in 2023, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) market is on a trajectory to reach $385.01 billion by 2031. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.70% from 2024 to 2031. Executives must consider this expansion as indicative of the sector’s increasing influence on global healthcare delivery.
Drivers of growth
Several factors contribute to the expanding IoMT market:
- The increased prevalence of chronic diseases necessitates more advanced monitoring and management solutions.
- Rising healthcare costs drive the search for more efficient healthcare delivery methods.
- There is a strong demand for patient-centered healthcare solutions that offer personalized care and improved patient outcomes.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of IoMT, particularly in areas like remote monitoring and telemedicine, which are becoming integral to healthcare strategies.
Challenges
Despite the promising growth, the IoMT sector faces several challenges:
- Data security is a top concern, as the handling of sensitive health data requires comprehensive protection measures to maintain patient confidentiality.
- Interoperability issues arise from the diverse vendor-specific standards and the prevalence of legacy systems in healthcare facilities, creating data silos that impede data integration.
- There is a pressing need for standardized regulations to facilitate the integration of IoMT solutions across different healthcare systems and devices.
Benefits and applications of IoMT
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
IoMT facilitates the continuous monitoring of patients’ vital signs and overall health status. Wearable devices equipped with sensors can transmit data directly to healthcare providers. For example, Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) for diabetes management send real-time glucose levels to doctors, allowing for immediate adjustments to treatment plans.
IoMT devices, such as CGMs and smart inhalers, are improving the management of chronic conditions. These technologies reduce the frequency of medical interventions and significantly improve patients’ quality of life by allowing better self-management and proactive care.
Personalized and proactive healthcare
IoMT’s capacity to use health data helps with the creation of personalized treatment plans. Wearable devices monitoring cardiovascular metrics allow healthcare providers to tailor treatments to individual patient needs, improving the precision and effectiveness of healthcare interventions.
Utilizing machine learning and predictive analytics, IoMT identifies potential health risks before they become critical. Such capabilities facilitate early intervention, reducing the likelihood of severe complications and the need for emergency healthcare services.
IoMT also transforms diagnostic processes by expanding on remote monitoring. Wearable ECG monitors, for instance, allow for the continuous transmission of heart data, facilitating remote assessments and early detection of potential issues.
Further, IoMT has removed geographical barriers through telemedicine, making healthcare services more accessible, especially for patients in remote locations or those with mobility constraints. Virtual consultations have become more common, improving access to healthcare advice and treatment adjustments without the need for physical travel.
Complexities and challenges in IoMT implementation
Data security and privacy concerns
Leaders in the healthcare sector recognize that IoMT involves the continuous collection and transmission of sensitive health data. Encrypting this data and ensuring secure storage are not just best practices but are fundamental requirements to protect patient confidentiality. Healthcare providers must adhere to stringent data protection regulations. Standards such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the Digital Information Security in Healthcare Act (DISHA) in India are not mere guidelines but mandatory frameworks that dictate how patient information must be handled securely. As IoMT expands, the complexity of safeguarding this data increases, necessitating advanced cybersecurity measures to defend against breaches and unauthorized access.
Interoperability challenges
Interoperability remains a major challenge in integrating IoMT into existing healthcare systems. The lack of standardized communication protocols often leads to the creation of data silos, where crucial patient information is trapped within specific devices or software, unable to be shared across the broader healthcare system. Many healthcare facilities operate with legacy systems that were not designed to communicate with the newer IoMT technologies. Addressing these issues requires substantial investment in upgrading or replacing incompatible systems and careful strategic planning to ensure that new and old technologies can work together effectively.
Integration with existing workflows
The introduction of IoMT technologies into established healthcare processes can disrupt existing workflows, leading to potential inefficiencies or errors if not managed carefully. Healthcare organizations must plan meticulously and train their staff adequately to integrate these new technologies. Smooth transition strategies are vital to minimize disruptions and maintain the continuity of patient care. This process often involves re-evaluating current procedures and determining how IoMT can complement or replace existing practices to improve efficiency and patient outcomes.
Cost considerations
Investing in IoMT technology involves significant upfront costs, including expenditures on new devices, infrastructure upgrades, and staff training. For healthcare executives, demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of these technologies is essential to secure organizational buy-in and funding. While the long-term benefits of IoMT can be substantial—such as reduced hospitalization rates, improved patient outcomes, and enhanced operational efficiency—articulating and quantifying these benefits upfront can be challenging. Healthcare leaders must present a compelling financial case that balances initial expenditures against expected gains from IoMT adoption.
Ethical and social implications
The deployment of IoMT raises important ethical considerations, particularly regarding informed consent for continuous data monitoring. Patients must be fully informed about how their data will be used and must give their explicit consent to this monitoring. Beyond individual consent, there are broader social implications to consider. The adoption of IoMT might exacerbate health disparities if not implemented thoughtfully. Disparities in access to technology can lead to unequal healthcare outcomes. Making sure that IoMT benefits all patients equally requires a concerted effort to address potential biases in data collection and interpretation and to make these technologies accessible across different socio-economic groups.
How Siam Computing can assist with IoMT integration
Siam Computing recognizes that each healthcare facility has unique needs and operational workflows. The company specializes in developing customized IoMT solutions that align specifically with the individual requirements and goals of each client. Siam Computing depends on the comprehensive integration of diverse IoMT devices, breaking down information silos and creating a unified healthcare ecosystem. This approach allows for the flow of patient data across different platforms and devices, giving healthcare providers a holistic view of each patient’s health journey.
Siam Computing prioritizes a privacy-first approach in all its IoMT solutions. The company implements comprehensive data security measures that comply with the highest industry standards, so that all patient data remains secure and private. Whether adhering to HIPAA, DISHA, or other local regulations, Siam Computing builds solutions that maintain the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive health information. This commitment to security helps build trust among healthcare providers and patients alike, making it easier to adopt and rely on IoMT technologies.
Understanding the importance of maintaining efficient operations, Siam Computing designs its IoMT solutions to integrate with existing healthcare workflows. The goal is to improve, not disrupt, the daily activities of healthcare providers. Siam Computing provides ongoing support and training, meaning that healthcare teams are confident and proficient in using the new technologies. This support helps minimize the learning curve and operational disruptions, leading to a smoother transition and more immediate realization of IoMT benefits.
To minimize the financial risks associated with implementing new technologies, Siam Computing offers innovative risk-sharing engagement models. These models include revenue-share payment options that align the company’s compensation with the actual benefits realized by the healthcare facility from IoMT adoption. Such models demonstrate Siam Computing’s commitment to the long-term success and financial viability of its IoMT solutions, making it easier for healthcare organizations to invest in these technologies with confidence.
Closing thoughts
The integration of IoMT is a strategic necessity for modern healthcare, offering a range of benefits from improved patient care to enhanced operational efficiencies. As the sector continues to grow, the challenges of data security, interoperability, workflow integration, cost, and ethical considerations remain focal points for executives. Siam Computing invites healthcare leaders to collaborate on implementing IoMT solutions, aiming to create a connected patient-care ecosystem that prioritizes the patient experience. The company’s tailored approach ensures that each healthcare facility can maximize the benefits of IoMT while overcoming the common barriers to technology adoption.